In the pursuit of a healthier lifestyle – including a healthy weight – many individuals find themselves on a quest to understand the intricacies of metabolism. This can be especially true as we age – a lot of people believe their metabolism slows after a certain age – like 40, 50, 60 – or that events in aging like menopause automatically cause slow metabolism, making fat burning more difficult for the body or leading to a person developing metabolic syndrome. So what exactly is metabolism, how can it be increased, and why does it matter for weight loss?
Metabolism refers to the complex set of chemical processes that occur within the cells of living organisms to sustain life. It involves the conversion of food into energy, which is essential for various physiological functions such as maintaining body temperature, supporting organ function, enabling physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Want to know more about metabolism and how to improve it? Learn more about our provider-guided weight loss program.
Metabolism and Weight Loss
Understanding the relationship between metabolism and weight loss is crucial for those aiming to shed excess pounds. Several key factors contribute to this connection:
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR): BMR represents the energy expended by the body at rest to maintain basic physiological functions, such as breathing, circulation, and cell production. Individuals with a higher BMR burn more calories even when at rest, making it easier for them to maintain or lose weight.
Caloric Expenditure: The total calories burned by the body are influenced by factors beyond BMR, including physical activity and the thermic effect of food (TEF). Regular exercise boosts caloric expenditure, while the TEF accounts for the energy required to digest, absorb, and process nutrients from food.
Metabolic Efficiency: Some individuals naturally possess a more efficient/fast metabolism, allowing them to process and utilize calories more effectively. Others may have a slower metabolism, making it easier for them to gain weight. Factors influencing metabolic efficiency include genetics, age, and hormonal balance.
Boosting Metabolism for Weight Loss
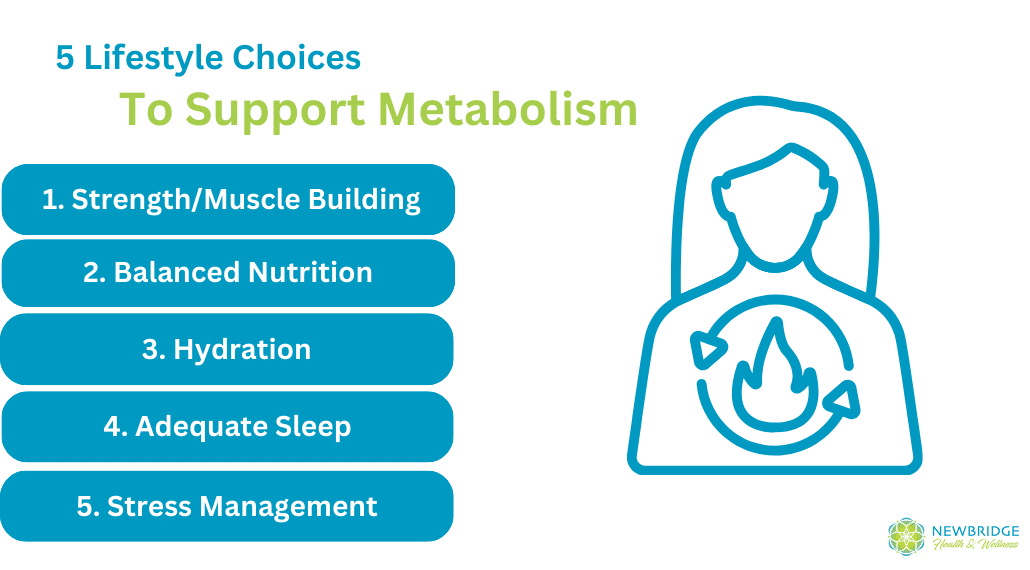
While genetic factors play a role in determining metabolic rates, several lifestyle choices can positively impact metabolism and aid in weight loss:
- Strength Training and Building Muscle: Engaging in both cardiovascular and strength training exercises can elevate BMR and contribute to overall caloric expenditure. More specifically, there is a direct correlation to muscle tissue and metabolic rate! Basically, the more muscle you have, the more affect your metabolic rate will operate at. Getting in strength training of some kind at least twice a week is a great way to start replacing fat mass with lean muscle mass!
- Balanced Nutrition: Consuming a well-balanced diet with an appropriate mix of macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) is essential for supporting metabolism. Adequate protein intake is particularly important, as it contributes to muscle maintenance and repair. It also takes longer to digest and requires greater effort by the body to break down, which actually means protein digestion will burn more calories compared to eating lots of simple carbohydrates. It’s important to note that every person’s dietary needs are based on their unique physiological needs. Cookie cutter diets are not a solution for weight loss and foods that increase metabolism for one person may not do the same for another.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is crucial for optimal metabolic function. Water is involved in many metabolic processes and can help with appetite control, indirectly influencing weight management. Just as importantly, electrolytes are also needed for the ideal balance of fluids. Electrolytes can be incorporated either with food or with a drink mix.
- Adequate Sleep: Quality sleep is integral to metabolic health. Lack of sleep can disrupt hormonal balance, leading to increased appetite and decreased energy expenditure, making weight loss more challenging. By establishing a bedtime routine and creating a sleeping space that is dark, cool, and comfortable, you can support getting enough quality sleep.
- Stress Management: Stress management significantly influences metabolism through hormonal responses, with chronic stress releasing cortisol and adrenaline, contributing to elevated blood sugar and insulin resistance. Changes in appetite and food choices during stress can impact weight gain and metabolic health, and physical activity, essential for metabolism, may be either promoted or hindered by stress. Techniques like meditation can help mitigate these effects by promoting relaxation and balancing the autonomic nervous system.
Metabolism is a multifaceted process that plays a pivotal role in weight management. While genetics do influence metabolic rates, lifestyle choices such as regular exercise, balanced nutrition, proper hydration, sufficient sleep, and managed stress levels can positively impact metabolism and contribute to successful weight loss. In other words, healthy and efficient metabolism is not as simple as having “fast” metabolism or taking a quick-fix route like going on a singular diet or exercising more. By understanding and optimizing the factors outlined above, individuals can embark on a journey towards a healthier and more sustainable lifestyle, including healthy and sustainable weight loss.
Do you need to lose weight? Learn more about our provider-guided weight loss program. We offer group and individual programs. Options for hybrid or telehealth available. Call (612) 730-2237 for more information.


